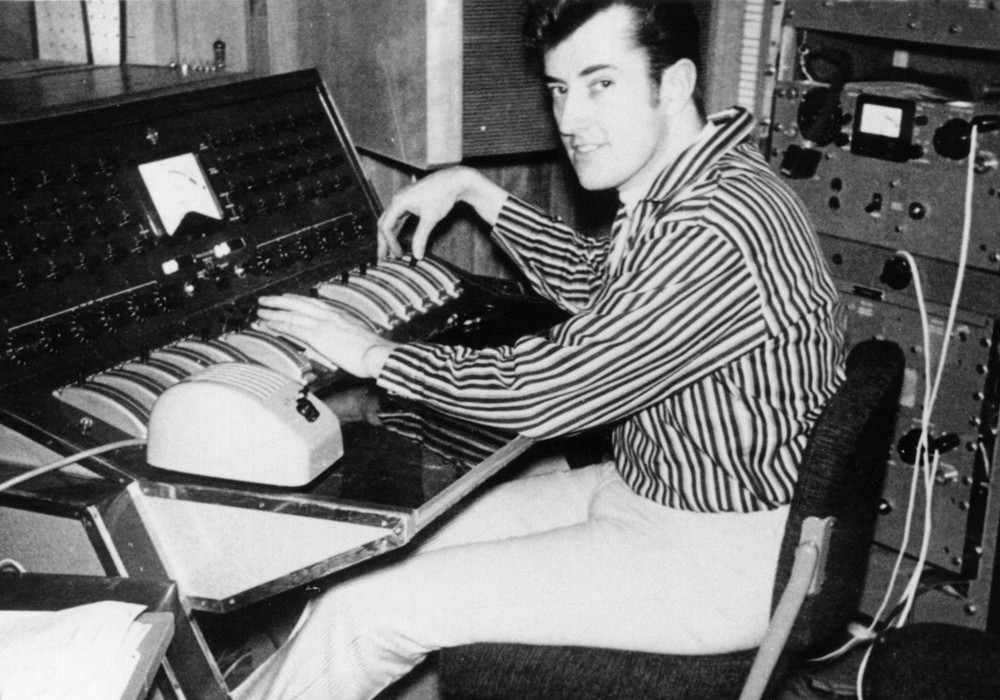
Fleetwood Mac’s Rumours came out right before I started high school. I remember most of my graduating class (not including me!) singing “Dreams” at our ceremony in a park by a local creek. Growing up in Northern California, we knew that two members of the band, Lindsey Buckingham and Stevie Nicks, had come from our neck of the woods, and watching the group become one of the biggest selling rock bands ever was dizzying. When they came out with Tusk a little over two years later, I bought the double LP and absorbed it like teenagers do. I knew something different was going on with these songs, but it was years before I realized what Lindsey Buckingham was doing, and why someone would find creativity in a home studio they might not otherwise. Lindsey’s new self-titled album, written, produced, mixed, and recorded in his home studio, is another classic example of his best work, and it was an honor to talk to him about his process.
Tape Op is about music recording in all kinds of scenarios. Ever since I started it, you’ve been in the back of my mind as the perfect interview.
Well, I do have my own methods; that’s for sure! [laughter]
Exactly. I wanted to talk to you a bit about all of your various personal recording scenarios.
Sure.
It’s well-known that a lot of home recording happened around the Tusk era, but did you have home recording setups before that, in the Buckingham/Nicks era, or in the Bay Area before that?
I did. When I was a late teenager and was in the band [Fritz] up in Northern California – that Stevie [Nicks] and I were both in, I was playing bass – I had an old commercial Sony 2-track. It had that sound-on-sound feature, where you could take one recording, say on the left channel, and then bounce it over to the right channel as you were recording something over it. I could begin to get a multitrack effect, one track at a time, which is pretty much the way that Les Paul [Tape Op #50] did it. That was his method and example that probably hit home with me. Then, a little bit later, probably about when I was 20 or 21, I acquired an Ampex AG-440 4-track, which obviously still had limitations. But hey, The Beatles cut Sgt. Pepper’s… on those, so it opened up the whole idea. It gave me much more flexibility. I was already into what I would call that “painting process” as early as that point, where I was putting things down all by myself, and doing the architecture around a song.
Did that influence the way you arrange guitars? I’ve interviewed Ken Caillat [Tape Op #96] before about how you put little filigrees and figures in; sometimes they are very simple parts to build a whole.
Right. Well, so much of my function in Fleetwood Mac was to take raw material and fashion it into a sound. I had the vision to do that, and I apparently had the tools to do that. Much of that was based around having a ground-up familiarity with a self-sufficiency, if you will; doing it myself and then bringing that into a more communal arena, for sure. So yeah, absolutely.
Did you have a home setup around the time of the self-titled Fleetwood Mac album?
When we first joined Fleetwood Mac, all of Stevie’s songs and my songs were already demoed out on my AG-440. That album only took a few months to do, and part of that was Keith Olsen [Tape Op #33] being in control of the engineering, as well as overseeing that things didn’t get too – shall we say? – self-indulgent. There was a lot at stake for them, because they were almost ready to be booted by Warner [Bros.] before we joined. They’d had so many non sequitur albums. The ability to make that album so quickly was largely due to the fact that all of Stevie’s and my material had been blocked out. What you hear on the record would be very close to what the demos were like, of course without John [McVie] and Mick [Fleetwood] as the rhythm section. I didn’t get a 24-track until a bit later, until there was a little bit more money coming in. Somewhere in the middle of the Rumours process is when I probably got one.
Right. That must have been a big step. A 24-track tape deck is nothing without a console, and then you need speakers and something to mix to.
I first got a 24-track and the machine at my house, [the one] that I did most of the work on my songs that ended up on Tusk. I would start these tracks as paintings, and then discover and find something which was a little bit more to the left. Then I’d bring them in for the band to add to. What’s funny is that I did not have a proper console at that time. I had enough channels to be able to play everything [back] at once, but it wasn’t a large thing. It was more...